People are looking for a system that enhances trust in financial transactions and record-keeping, and blockchain technology is here to meet that need. Read this article of TechTrends to find the answer to What is Blockchain and how does it work?
Blockchain’s system of information recording opened a new door to making it almost impossible to alter, hack or cheat the system in any sort. Isn’t that something we all need? Security? Notwithstanding the many efforts made to build digital money in the past, they all have struggled, with the prevailing problem being trust. Here was when the blockchain emerged. For understanding the growing interest, it is helpful to know the answer to these questions: What is Blockchain? How does blockchain work?
What Is Blockchain?

Blockchain can be described as a distributed ledger technology (DLT) and a database that keeps transactional records while ensuring users benefit from its security, transparency, and decentralization. We can mention their crucial role in cryptocurrency systems, like Bitcoin, of their main features. It is innovative in ensuring the fidelity and security of data-recording, giving trust with no need for a third party.
One crucial aspect that separates a blockchain from a typical database is the data structure. Information is recorded in groups that are known as blocks. As its name implies, the blockchain forms a chain of data when its storage is filled. How? It will be closed and linked with the last filled block, and the cycle continues.
To elaborate on What is Blockchain? in other words, a typical database is structured into tables. In contrast, a blockchain strings them together in blocks that innately create an irreversible timeline of data when put in a decentralized nature. Once filled, a block is added to this timeline after receiving an exact timestamp.
Read more: Best Cryptocurrencies to invest in 2022 and beyond
How Does Blockchain Work?
Blockchain’s primary purpose is to permit the recording and distribution of digital information without any editing. Through this method, blockchain became the solid foundation for a DLT due to its immutable ledgers or transaction records that cannot be changed, deleted, or destroyed.
In 1991, there was a proposal for blockchain as a research project. Therefore, the notion predated its worldwide application in 2008 by powering Bitcoin, and it was brought to real-world use like explained in the paper by Satoshi Nakamoto titled “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System.” However, it found many other uses beyond that, when various cryptocurrencies, decentralized finance applications, non-fungible tokens (NFTs) and smart contracts were created. After reading about blockchain definition and how it works, you might also want to check the article on “Top 10 Most Expensive NFTs Ever Sold.”
After What is Blockchain, the next question is “How does blockchain work?” to explain it in steps, we will use Bitcoin as an instance:
- The sale and purchase of Bitcoin are added and transmitted to nodes, which are networks of powerful computers.
- The nodes compete to confirm the transaction using computer algorithms, known as Bitcoin mining. If a miner completes a new block successfully, they will be rewarded with Bitcoin, paid through newly minted Bitcoin, and network fees passed on to the buyer and seller.
- The cryptographical confirmation of the purchase will go on a block on the distributed ledger. The majority of the network should also confirm the sale.
- After that, the block is linked to all the last blocks of Bitcoin transactions permanently, using a hash, which is a cryptographic fingerprint. The sale is then processed.
Blockchain Features
Having a solid understanding of what is blockchain, you should know that this innovative technology does not serve as a backup network for cryptocurrencies; however, it has more to offer. But what are the top blockchain features that make it irresistible to many? Let’s dig a little deeper into everything you need to know about blockchain.
Decentralization
One of the main features explained in the article what is Blockchain? is its decentralized benefit. Picture a company with a server farm, equipped with 10,000 computers used to keep a database, having all the information of its clients. All computers are in a warehouse building owned by this company, with unlimited access to all the information. Isn’t that a failure when the electricity goes out? What happens when the internet connection is severed? Or what if it gets destroyed in a fire? In any of these cases, the information will be corrupted or lost.
On the other hand, blockchain allows the data stored in that database to be sent among many network nodes at different places. Not only does it create redundancy, but it also keeps the fidelity of the information within. For example, if someone attempts to change a record at one location, the other nodes would not be changed. All nodes will work together, cross-referencing and pinpointing the node that contains incorrect data. Exact and transparent order is established in a system like a blockchain.
Due to this, the data and history will be irreversible. In addition to transactions of cryptocurrency data, a blockchain can keep various kinds of information, such as legal contracts, state identifications, or the product inventory of a company.
Transparency
Given the decentralized nature of Bitcoin’s blockchain, through an individual node or blockchain explorers, all transactions can be transparently viewed. Each node’s chain copy is updated when new blocks are processed and added. In other words, it allows you to track Bitcoin wherever it goes.
For instance, exchanges were hacked, and many who had Bitcoin lost everything. Whereas the hacked can be totally anonymous, the taken Bitcoin can be easily traced. If the stolen Bitcoins were to be spent or moved, it would be revealed.
Furthermore, the records maintained in the Bitcoin blockchain (and many others) are encrypted, with the owner being the only one that can decrypt it. This means that blockchain users can remain anonymous and preserve transparency.
Security
One of the blockchain features is its decentralized security and trust, achieved in several ways. First, new blocks are saved in chronological order, meaning they are stored at the end of the blockchain. Following the addition of a block, it is tough to go back and change the block’s contents only if the majority of the network has reached an agreement to do so. The reason is that every block contains its own hash and the previous block’s hash along with the time stamp. Through a mathematical function that changes digital information into a string of numbers and letters, hash codes are made. Should that information be edited in any way, the hash code will change, too.
Imagine that a hacker, who runs a node on a blockchain network, aims to steal cryptocurrency from everyone else on the network and changes a blockchain. Should they change their own copy, it will no longer align with others’ copies. By cross-referencing their copies with each other, everyone can see the one that stands out, with the hacker’s version being labeled illegitimate.
To be successful in such a hack, the hacker needs to have control over 51% or more copies at the same time for the new copy to be the majority copy and for the chain to accept it. This attempt needs many resources and money, as redoing all blocks requires different time stamps and hash codes.
The cost for doing something like this would be impossible due to the high growth and many cryptocurrency networks’ sizes. Aside from being expensive and fruitless, network members would notice such drastic changes. They can then go to a new chain version, making the attack pointless.
Different Types of Blockchains
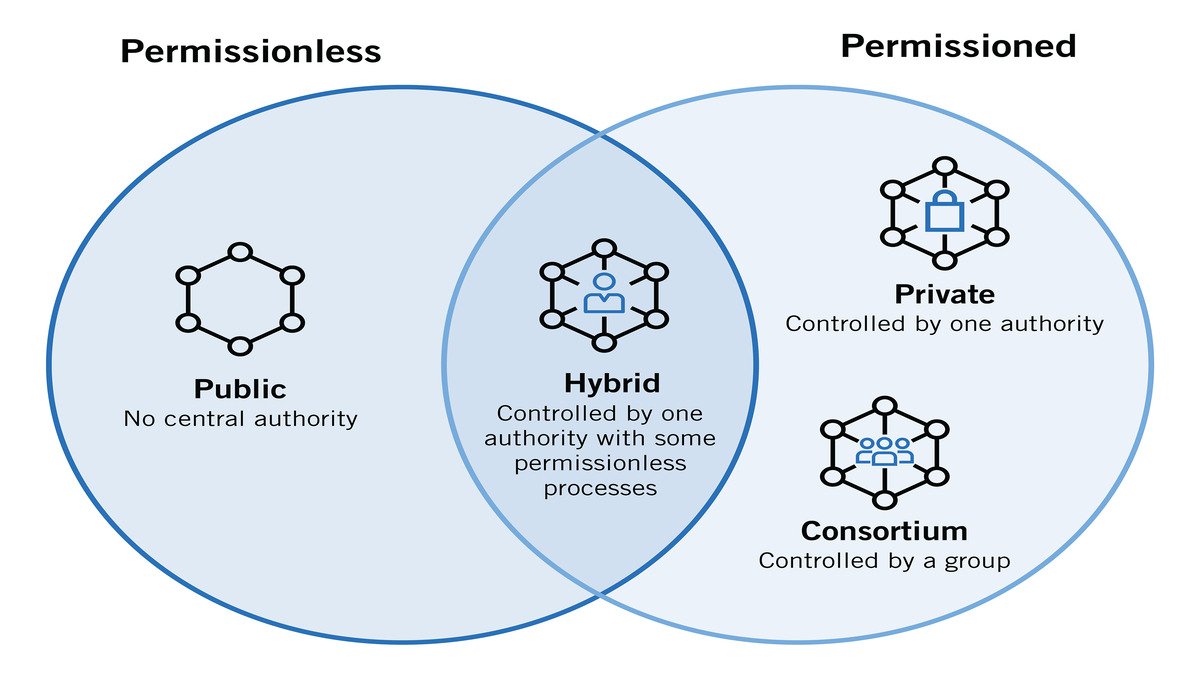
Having learned all about What is blockchain?, “How does blockchain work?” and “What are blockchain features?” it is time to dive into the four different types of blockchain structures:
- Public Blockchains
This type of blockchain permits anyone to enter. In other words, they are permissionless and totally decentralized. All public blockchain nodes have equal access and can create and validate new blocks of information.
Currently, investors and collectors mainly use public blockchains, such as Bitcoin, Ethereum, and Litecoin, in exchanging and mining cryptocurrency. When there is a transaction request, the nodes “mine” for cryptocurrency by creating blocks. The miner nodes, or the new era bank tellers, then get some cryptocurrency as a reward for their hard work.
- Private Blockchains
Private blockchains, also called managed blockchains, on the other hand, are permissioned and controlled by one organization. The central authority in this type of blockchain decides who can be a node. It also doesn’t grant equal rights to each node for performing functions. This type of blockchain is partially decentralized since they limit public access. Among the examples, there are Ripple and Hyperledger.
These two different types of blockchains have some disadvantages; while public blockchains have a longer validation time for new information, private blockchains have fewer, and they are more vulnerable when it comes to fraud. However, the development of consortium and hybrid blockchains aimed to solve these drawbacks.
- Consortium Blockchains
A group of organizations governs permissioned consortium blockchains. Compared to private blockchains, Consortium blockchains have more decentralization, which seals more security. However, many organizations need to cooperate in setting up consortiums. In addition, supply chains members might not have the required technology or infrastructure for implementing blockchain tools. For those that do, there is the issue of costs being too steep for digitizing their information.
The enterprise software firm R3 has developed a well-known set of consortium blockchain solutions for the financial services industry and beyond. CargoSmart has developed the Global Shipping Business Network Consortium.
- Hybrid blockchains
Many suggest this type of blockchain for organizations that want the best of both worlds, which combines both private and public blockchain elements. A single organization controls it; however, the public blockchain’s level of oversight is performed here for transaction validation. IBM Food Trust serves as an example of a hybrid blockchain, with its purpose being efficiency in the entire food supply chain.
Blockchain, Digital Currency, Cryptocurrency and Bitcoin Explained
After knowing the answer to the question what is blockchain?, it is good to understand why blockchain, cryptocurrency, and Bitcoin are frequently lumped together along with the digital currency. They are even used interchangeably sometimes.
Despite being under the umbrella of distributed ledger technology, each is distinctive.
- Blockchain, as mentioned earlier, is a technology with a decentralized digital ledger that allows many parties to exchange in a secure, immutable way.
- Digital currency is any form of currency that is just in digital format, like the digital money and governments and central banks and cryptocurrency issue it. Other names can be cyber cash, electronic money, or electronic currency.
- Cryptocurrency, a subset of digital currency, is considered a digital asset exchang on a blockchain network. Government entities do not issue crypto, but it is like a token issued by private entities or groups, used in paying for items sold by those in charge of the network. The first and the most famous cryptocurrency is Bitcoin
What Is Next for Blockchain?
Blockchain has started making a name for itself at the age of 27 since there are a lot of practical applications for this technology to venture. This latest buzzword that many investors are familiar with aims to bring accuracy, efficiency, and security to businesses and government operations.
Going into its third decade, it is only a matter of time until companies will catch on to the technology and it is not a matter of if. Therefore, the upcoming years are essential in the growth of blockchain. This article aimed to provide you with a comprehensive guide on what is blockchain, how blockchain works, and what different types there are. It will walk you through anything you need to know to help you gain general knowledge on the matter if you see any potential in this technology for future investments.
